Cumulative data modeling (Part 1)
The going approach to model data is drawing your ER Diagram and map it to your persistence, be it normalized in a RDBMS or an entry in a NoSQL store.
A slice of cake
Walking through the use case of a cheese cake factory, slightly simplified. All process steps happen in batches, but batch sizes are not synchronized. E.g. dough mixing produces 0.8 - 1.4 times the baking capacity.
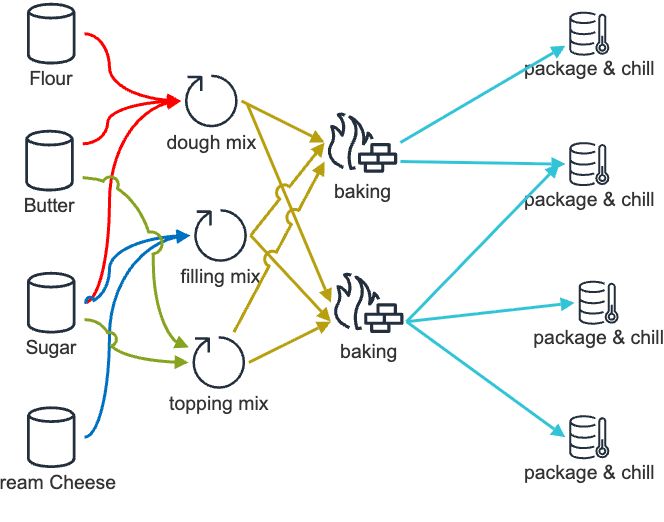
The corresponding data model would look like this:
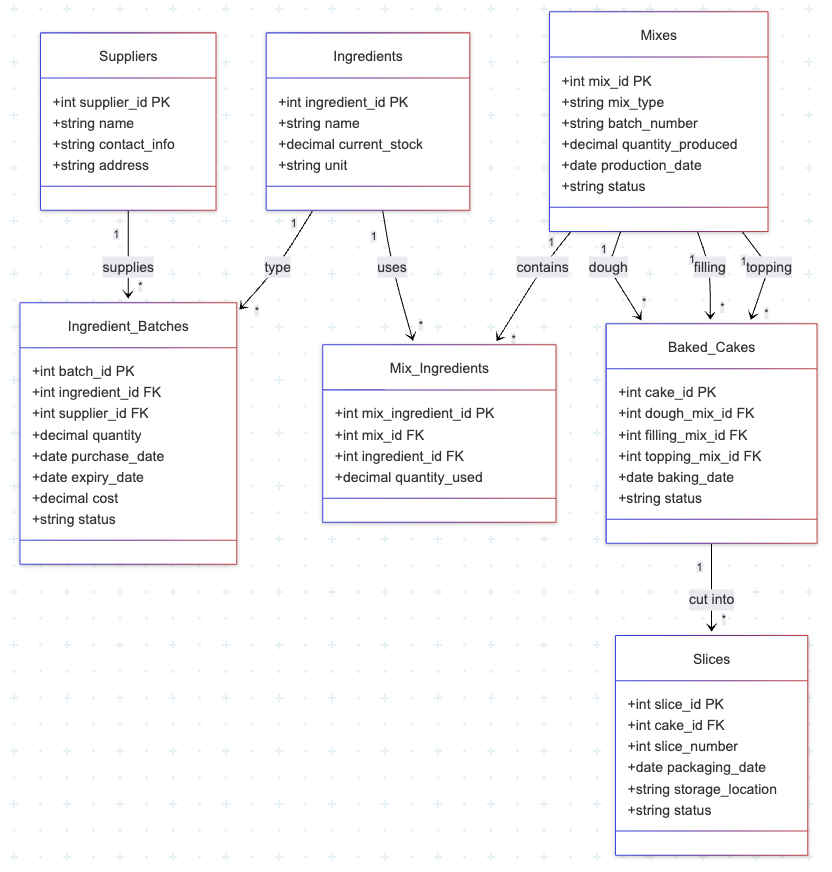
Now imagine a customer wants to know if the slice is made with cheese from "happy cows", which is a trade certification some of the suppliers have. A simple SQL solves it:
SELECT
s.slice_id,
ROUND(
(SUM(CASE WHEN sup.HappyCowCertified = TRUE THEN mi.quantity_used ELSE 0 END) /
SUM(mi.quantity_used)) * 100,
2
) AS happy_cow_percentage
FROM Slices s
JOIN Baked_Cakes bc ON s.cake_id = bc.cake_id
JOIN Mix_Ingredients mi ON (
mi.mix_id = bc.dough_mix_id OR
mi.mix_id = bc.filling_mix_id OR
mi.mix_id = bc.topping_mix_id
)
JOIN Ingredients i ON mi.ingredient_id = i.ingredient_id
JOIN Ingredient_Batches ib ON mi.batch_id = ib.batch_id
JOIN Suppliers sup ON ib.supplier_id = sup.supplier_id
WHERE s.slice_id = 'someSliceId'
AND i.name = 'Cream Cheese'
GROUP BY s.slice_id;
Another day another challenge: a batch from a supplier was sub standard and you need to recall all slices made with it. SQL to the rescue again:
SELECT DISTINCT
s.slice_id,
s.storage_location
FROM Slices s
JOIN Baked_Cakes bc ON s.cake_id = bc.cake_id
JOIN Mix_Ingredients mi ON (
mi.mix_id = bc.dough_mix_id OR
mi.mix_id = bc.filling_mix_id OR
mi.mix_id = bc.topping_mix_id
)
WHERE mi.batch_id = 'someBadBatchId'
ORDER BY s.slice_id;
As long as as bakery control system has this baked in (pun intended) or you have your residential SQL jockey on speed dial, all is well (keep in mind: the real data model is way more complex), but there might be a better way, slightly unconventional. Stay tuned for part 2.
Posted by Stephan H Wissel on 23 January 2026 | Comments (0) | categories: CouchDB Development NoSQL SQL