Long Term Storage and Retention
Not just since Einstein time is relative. For a human brain anything above 3 seconds is long term. In IT this is a little more complex.
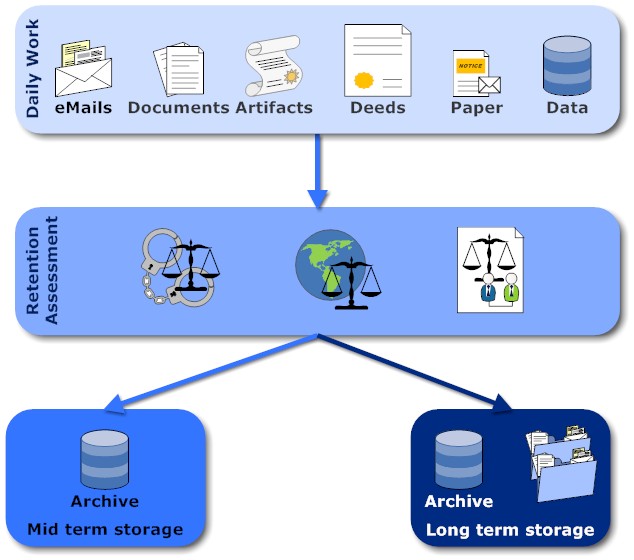
Once a work artefact is completed, it runs through a legal vetting and it either goes to medium or long term storage. I'll explain the difference in a second. This logical flow manifests itself in multiple ways in concrete implementations: Journaling (both eMail and databases), archival, backups, write-once copies. Quite often all artifacts go to medium term storage anyway and only make it into long term storage when the legal criteria are met. Criteria can be:
On the other hand, in a long-term storage scenario you can't rely on a specific software for either search or artifact rendering. So you need to plan a little more carefully. Most binary formats fall short of that challenge. Furthermore your artefacts must be able to "carry" their meta data, so a search application can rebuild an access index when needed. That is one of the reasons why airline maintenance manuals are stored in DITA rather than an office format (note: docx is not compliant to ISO/IEC 29500 Strict).
The problem domain is known as Digital Preservation and has a reference implementation and congressional attention.
In a nutshell: keep your data as XML, PDF/A or TIFF. MIME could work too, it is good with meta data after all and it is native to eMail. The MIME-Trap to avoid are MIME-parts that are propriety binary (e.g. your attached office document). So proceed with caution
Neither PST, OST nor NSF are long term storage suitable (you still can use the NSF as the search database)
To be fully sure a long term storage would retain the original format (if required) as well as a vendor independent format.

Once a work artefact is completed, it runs through a legal vetting and it either goes to medium or long term storage. I'll explain the difference in a second. This logical flow manifests itself in multiple ways in concrete implementations: Journaling (both eMail and databases), archival, backups, write-once copies. Quite often all artifacts go to medium term storage anyway and only make it into long term storage when the legal criteria are met. Criteria can be:
- Corporate & Trade law (e.g. the typical period in Singapore is 5 years)
- International law
- Criminal law
- Contractual obligations (E.g. in the airline industry all plane related artefacts need to be kept at least until the last of that plane family has retired. E.g. the Boing 747 family is in service for more than 40 years)
-
Data Extraction
When your production system doesn't provide retention capabilities, how to get the data out? In Domino that's not an issue, since it does provide robust storage for 25 years (you still need to BACKUP data). However if you want a cross application solution, have a look at IBM's Content Collector family of products (Of course other vendor's have solutions too, but I'm not on their payroll) -
Findability
Now an artifact is in the archive, how to find it? Both navigation and search need to be provided. Here a clever use of Meta data (who, what, when, where) makes the difference between a useful system and a Bit graveyard. Meta data isn't an abstract concept, but the ISO 16684-1:2012 standard. And - YES - it uses the Dublin core, not to confuse with Dublin's ale -
Consumability / Resillience
Once you found an artifact, can you open and inspect it. This very much boils down to: do you have software that can read and render this file format?
On the other hand, in a long-term storage scenario you can't rely on a specific software for either search or artifact rendering. So you need to plan a little more carefully. Most binary formats fall short of that challenge. Furthermore your artefacts must be able to "carry" their meta data, so a search application can rebuild an access index when needed. That is one of the reasons why airline maintenance manuals are stored in DITA rather than an office format (note: docx is not compliant to ISO/IEC 29500 Strict).
The problem domain is known as Digital Preservation and has a reference implementation and congressional attention.
In a nutshell: keep your data as XML, PDF/A or TIFF. MIME could work too, it is good with meta data after all and it is native to eMail. The MIME-Trap to avoid are MIME-parts that are propriety binary (e.g. your attached office document). So proceed with caution
Neither PST, OST nor NSF are long term storage suitable (you still can use the NSF as the search database)
To be fully sure a long term storage would retain the original format (if required) as well as a vendor independent format.
Read more
Posted by Stephan H Wissel on 14 August 2014 | Comments (1) | categories: IBM Notes Software